Options
2.5D Clip-Surfaces for Technical Visualization
Journal
Proceedings of WSCG 2013: 21st International Conference in Central Europe on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Computer Vision
Date Issued
2013
Author(s)
Trapp, Matthias
D\"ollner, J\"urgen
Editor(s)
Skala, Václav
Abstract
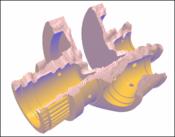
The concept of clipping planes is well known in computer graphics and can be
used to create cut-away views. But clipping against just analytical defined
planes is not always suitable for communicating every aspect of such visualization. For example, in hand-drawn technical illustrations, artists tend to communicate the difference between a cut and a model feature by using non-regular, sketchy cut lines instead of straight ones. To enable this functionality in computer graphics, this paper presents a technique for applying 2.5D clip-surfaces in real-time. Therefore, the clip plane equation is extended with an additional offset map, which can be represented by a texture map that contains height values. Clipping is then performed by varying the clip plane equation with respect to such an offset map. Further, a capping technique is proposed that enables the rendering of caps onto the clipped area to convey the impression of solid material. It avoids a re-meshing of a solid polygonal mesh after clipping is performed. Our approach is pixel precise, applicable in real-time, and takes fully advantage of graphics accelerators.
used to create cut-away views. But clipping against just analytical defined
planes is not always suitable for communicating every aspect of such visualization. For example, in hand-drawn technical illustrations, artists tend to communicate the difference between a cut and a model feature by using non-regular, sketchy cut lines instead of straight ones. To enable this functionality in computer graphics, this paper presents a technique for applying 2.5D clip-surfaces in real-time. Therefore, the clip plane equation is extended with an additional offset map, which can be represented by a texture map that contains height values. Clipping is then performed by varying the clip plane equation with respect to such an offset map. Further, a capping technique is proposed that enables the rendering of caps onto the clipped area to convey the impression of solid material. It avoids a re-meshing of a solid polygonal mesh after clipping is performed. Our approach is pixel precise, applicable in real-time, and takes fully advantage of graphics accelerators.
File(s)
Loading...
Name
clipping.pdf
Size
10.33 MB
Format
Adobe PDF
Checksum
(MD5):b434731cbd4373ad6b439f49404faf34
Loading...
Name
rcp-teaser-cropped-final.png
Size
92.74 KB
Format
PNG
Checksum
(MD5):a1b82a3d1b847eb860081f76b7560d88